대학생때와 졸업 후 1년간 오직 JAVA만 사용해 안드로이드 개발을 했더니 머릿속에서 자바스크립트가 일정부분 날아간 기분이 든다. 그래서 오랜만에 프로그래머스 1단계 문제를 풀어봤다가 생각보다 심하다는걸 깨달았다.. React, node.js에서는 사실 늘 쓰는 function과 Mongoose함수만 주구장창 사용하기 때문에 JS 실력이 늘어날 수 없었던 것 ㅠㅠ 게다가 React는 아주 기초적인 js 문법만으로도 휘황찬란한 웹을 만들 수 있다. 이게 나의 뇌를 마취시킨 주 원인이었던듯 하다..
기념삼아 JS ES6 문법을 공부하고 기록하기로 했다. 평생 할 줄 알았던 Java는 이제 안녕~~...(회사들어가면 하게 될지도 모르겠지만..~)
this
자바스크립트에서 this는 상황에 따라 다른 것을 가리키게 된다. 먼저 함수나 변수를 전역 공간에서 만들면,
js는 함수나 변수를 {window}에 보관한다. window는 global object, 즉 전역변수 보관소이다.
따라서 아래 1, 2, 3의 경우들에서 this는 window를 가리키게 된다.
1. 그냥 사용하거나, 일반 함수 안에서 사용할 경우 this는 window를 가리킨다.
<script>
console.log('그냥 this', this)
function test() {
console.log(this)
}
test()
</script>
use strict는 Js를 좀 더 엄격하게 사용하게 해 주는 설정값이다. 이 경우, 함수 속 this는 undefined로 출력된다.
<script>
'use strict'
console.log('그냥 this', this)
function test() {
console.log('function 속 this',this)
}
test()
</script>
2. 오브젝트 내의 함수 안에서 사용하면, '그 함수를 가지고 있는 오브젝트'를 뜻한다.
<script>
console.log(this)
let testObject = {
data:'Chali',
testFunction : function() {
console.log('test Object 내 testFunction', this)
}
}
testObject.testFunction();
</script>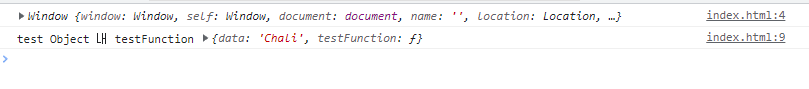
오브젝트 내의 오브젝트에 사용해도, 결과는 'this를 호출한 함수를 가지고 있는 오브젝트'를 가리킨다. (최상위 오브젝트가 아니라, 그 함수를 가지고 있는 개별 오브젝트라는 것을 잘 알아야 함.)
<script>
console.log(this)
let testObject = {
data: {
testFunction : function() {
console.log('test Object 내 testFunction', this)
}
}
}
testObject.data.testFunction();
</script>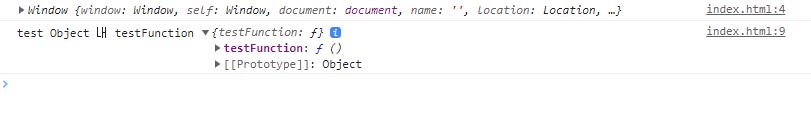
3. Arrow Function에서 사용된 this는 함수 밖에 있던 값을 사용한다.
<script>
console.log(this)
let testObject = {
data: {
testFunction : ()=> {
console.log('test Object 내 testFunction', this)
}
}
}
testObject.data.testFunction();
</script>
이번에는 window가 아닌 것을 가리키는 this를 알아보자.
1. constructor 내에서 사용하면, constructor 내에서 생성되는 오브젝트를 가리킨다.
<script>
function test() {
this.name = 'testName'
console.log(this.name)
}
let output = new test();
</script>(참고 : constructor에서 새로운 오브젝트를 생성하려면, new 키워드를 사용한다. function test()는 붕어빵 틀이고, output은 붕어빵 틀에서 구워낸 붕어빵이 되는 것이다.)

2. EventListener 속 this는 e.currentTarget을 가리킨다.
<button id="button">테스트 버튼</button>
<script>
document.getElementById('button').addEventListener('click',function(e) {
console.log('이벤트 리스너 속',this)
console.log('e.currentTarget',e.currentTarget)
})
</script>
3. eventListener 내의 콜백함수 속 this는 window를 가리킨다.
<button id="button">테스트 버튼</button>
<script>
document.getElementById('button').addEventListener('click',
function(e) {
let testArray = [1,2,3]
testArray.forEach(function(a) {
console.log(a,this)
})
})
</script>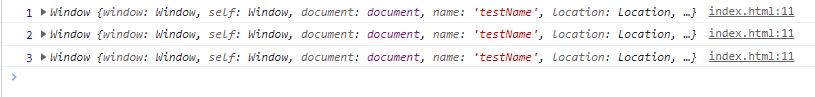
4. 오브젝트 내의 콜백함수 속 this는 window를 가리킨다. 화살표 함수가 되면, 상위의 this를 물려받는다.
<button id="button">테스트 버튼</button>
<script>
let testObj = {
number: [1,2,3],
testFunction : function() {
console.log('testFunction의 this', this)
testObj.number.forEach(function(){
console.log('testObj.number.forEacth(function)의 this',this)
})
}
}
testObj.testFunction();
</script>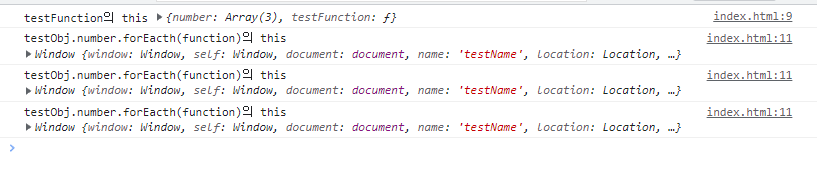
=> 그러나 콜백함수의 function을 Arrow Function, 즉 ()=> 으로 바꾸어주면 외부의 this값을 그대로 물려받아 사용한다. 따라서 화살표 함수는 this 키워드를 사용할 때 유용하다.
<button id="button">테스트 버튼</button>
<script>
let testObj = {
number: [1,2,3],
testFunction : function() {
console.log('testFunction의 this', this)
testObj.number.forEach(()=>{
console.log('testObj.number.forEacth(Arrow)의 this',this)
})
}
}
testObj.testFunction();
</script>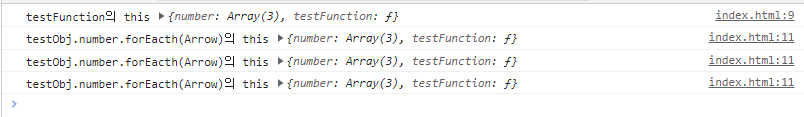
'JavaScript > JavaScript 기초' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Javascript ES6] 기초 문법 6. Spread Operator (0) | 2022.12.20 |
|---|---|
| [Javascript ES6] 기초 문법 5. Spread Operator (0) | 2022.12.20 |
| [Javascript ES6] 기초 문법 4. Template Literals, Tagged Literals (0) | 2022.12.20 |
| [Javascript ES6] 기초 문법 3. 변수 var, let, const (0) | 2022.12.07 |
| [Javascript ES6] 기초 문법 2. Arrow Function (0) | 2022.12.07 |

